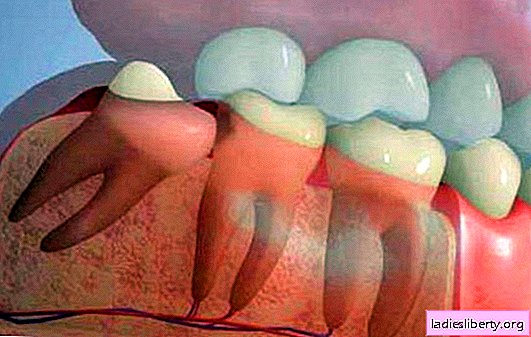
Toothache is perhaps one of the most unpleasant in ordinary life of a healthy person. Unbearable pain and discomfort cause the same amount of negative emotions when the wisdom tooth grows and the gums hurt.
This happens already in adults, about the age of 18 to 32 years. However, not all adults can boast a smile on all 32 teeth. There are times when wisdom teeth never appear, and a person has only 28 teeth.
Even preventative measures, such as regular visits to the doctor, do not help when the wisdom tooth grows and the gums hurt.
How do wisdom teeth grow?
The tooth of wisdom is an eight; it develops slowly and over many years.
If the remaining 28 teeth in a person appear from infancy, first in the form of milk, and then change to permanent, then the molars begin to develop when the jaw and its musculoskeletal tissue are already formed.
At the place of their appearance, teeth did not grow before. And the molars have to erupt in the already formed jaw and the whole gum, causing inflammation of the surrounding tissues, including the gums.
The relative softness and elasticity of the musculoskeletal tissue lasts up to 13 years.
Causes of pain in the growth of wisdom teeth
The causes of pain are:
1. Lack of space in the row for an erupting tooth, so the figure eight is not correctly positioned during eruption, exerting pressure on surrounding tissues and adjacent teeth. This occurs in more than 60%.
If you do not go to the dentist, you can lose neighboring teeth. There will be a shift in the entire series and the development of a malocclusion, which is very difficult to correct. In the future, you have to spend a long time on it.
2. In the process of growth of a wisdom tooth, part of it remains undercover mucous membrane - the so-called hood, under which food particles penetrate, difficult to remove when cleaning. This leads to the rapid multiplication of microbes and the development of the inflammatory process in the gum around the tooth.
In this case, you have to resort to excision of the hood. Otherwise, complications develop in the form of edema and suppuration of soft tissues.
Symptoms accompanying gum pain
When the gum hurts near the wisdom tooth, the pain is accompanied by:
• high temperature;
• swelling of the cheeks on the affected side or tongue;
• radiating to the ear, throat, head;
• difficulty swallowing or opening the mouth;
• suppuration of the surrounding musculoskeletal tissue.
A wisdom tooth grows and a gum aches - what to do
Since it is impossible to influence the immediate cause of the onset of pain, it is useful to know what methods can be applied if the wisdom tooth grows and the gum hurts. It is impossible to tolerate intolerable pain when teething wisdom. You should immediately contact your dentist to avoid complications. If there is no such possibility in the first two days, you can try means that alleviate the condition:
• soda-salt rinse: in a glass of hot water, dilute a teaspoon of salt and the same amount of soda. When the solution cools down and becomes warm, it is necessary to rinse your mouth, holding the solution near the growing tooth;
• furatsilin - antimicrobial agent: to rinse 2 tablets, dissolve in a glass of water;
• effective applications on the edematous oral mucosa in the place of the future tooth with anesthetic gels (Holisal);
• drink an anesthetic or a slice of a tablet to apply to a sore spot: Tempalgin, Analgin, Ketanov;
• herbal decoctions for rinsing from sage, plantain, calendula;
• calendula rinse solution: a teaspoon of alcohol solution in a glass of warm water;
• Lidocaine - vial - is a spray that can be sprayed on a painful place, the pain will temporarily subside;
• about antibiotics (Doxycycline, Linkomycin), you must consult a doctor, do not take them yourself.
It is important to know:
All solutions used for rinsing should be warm. It is strictly contraindicated to warm the inflamed place: this can lead to the spread of the purulent process.
But such measures are temporary and urgent, designed for the possibility of going to the doctor. They cannot solve the problem: qualified medical care is needed here.
Wisdom tooth extraction - indications for removal
If preventive measures have not been taken, removal of the third molar may be necessary. Indications for removal are:
• horizontal eruption of the eight;
• the molar is too close to the roots of adjacent teeth, which injures them;
• the growth of a wisdom tooth in the cheek, wounding its surface;
• with the "immersed" wisdom tooth - if the tooth has not erupted or partially erupted;
• high risk of developing a cyst or infection of surrounding tissues;
• an abscess;
• developed deep caries.
When the situation is delayed, the process can go far and you will have to carry out surgical intervention to remove these teeth until they finally violate the dentition.
After medical manipulations, the operation site is treated with antiseptics and antibacterial drugs. Rinsing is prescribed at home.
Diagnostic measures
Removal is based on:
• patient complaints;
• inspection;
• targeted x-ray examination of the wisdom tooth,
• if necessary - X-ray examination of the jaw;
• in severe or unclear cases - a circular orthopantogram that allows you to assess the condition of neighboring teeth or structural features of the jaw.
How long does the pain last after removing a wisdom tooth
If the wisdom tooth was removed at a stage when complications had not yet developed, the pain in this place after the termination of anesthesia would last about a day.
If the eight is removed in the process of complication, when there is already inflammation of the tissues and suppuration is developing, or the dentist had to open the mucous membrane and remove the remaining eight, piece by piece, the pain will continue for a long time. After two days, a maximum of up to a week, the pain will begin to subside.
Wisdom Tooth - Challenges in Growth
The wisdom tooth in the process of its development causes a whole series of problems:
1. Caries: due to the inaccessibility and difficulty of brushing, a large number of bacteria accumulate. In addition, wisdom teeth do not participate in the chewing process, which also contributes to the accumulation of bacteria and, with poor cleaning, leads to caries, which can subsequently affect neighboring healthy teeth.
2. Periodontitis and pericoronitis - inflammation of the gums and nearby tissues of a purulent nature, accompanied by:
• swelling and pain;
• fetid halitosis and taste;
• increase in temperature.
This is due to the presence of space between the erupting tooth and the gum, where, due to insufficient cleaning, pathogenic bacteria and food microparticles accumulate, leading to inflammation.
3. Periostitis and osteomyelitis is an inflammatory process in the periosteum and bone in the area of an erupting tooth.
4. Distilled tooth - in the wrong position. Such teeth lead to a violation of the dentition and bite, to damage to the mucous membrane of the cheek. These teeth are removed.
5. A refined tooth - not yet erupted, but already in the wrong position: it rests on the jaw bone or on the adjacent tooth and its root.
Pericoronitis is a serious complication
A wisdom tooth that causes pericoronitis carries a potential health hazard:
1. The formation of purulent exudate under the gum.
2. Permanent trauma of the edematous gums over the wisdom tooth.
3. The appearance of erosion and ulcers, worsening the condition of the gums and leading to severe pain in the cheek and gum.
After a short time, the process is aggravated:
• intoxication develops with high fever;
• "dental sore throat" - intense pain when swallowing like anginous, radiating to the ear and temple;
• pain when opening the mouth;
• an increase and tenderness of the submandibular lymph nodes.
The danger of this process is that the acute phase with a vivid clinical picture with a high immune status and ingestion of pus in the oral cavity can go into a chronic sluggish form. But with the next troubles in the body, the process can again aggravate and lead to a post-molar periostitis with severe intoxication and the inability to chew food and difficulty opening the mouth.
This is expressed in objective status:
• facial asymmetry;
• increase and pain in the submandibular lymph nodes;
• the skin is extremely pale;
• inability to open the mouth due to pain - the doctor has to open his jaw.
With the further development of a purulent process, the following may develop:
• phlegmon;
• sepsis;
• severe intoxication;
• death.
Given such severe complications, the preventive role of examinations at the dentist is difficult to overestimate.
Orthodontic dentists can determine from the age of 13 to 15 years whether pericoronitis will develop.
In many cases, an unformed wisdom tooth is easier to remove than one that already has a network of powerful, branched roots.
Therefore, timely access to a doctor will help to avoid these complications.











